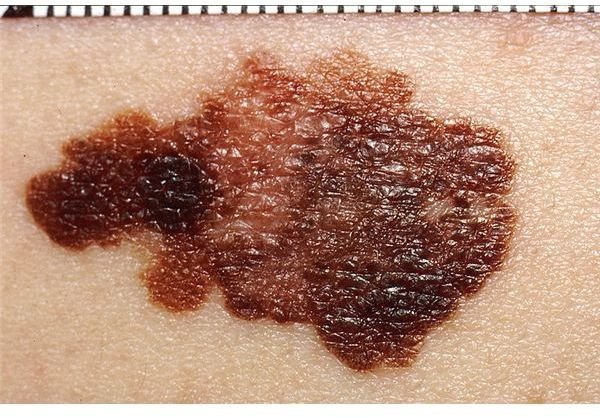
How Fast Does Melanoma Spread and What Should I Know About this Skin Cancer?
Melanoma is the most lethal and serious type of skin cancer, with the exception of certain rare skin cancers, due to melanoma being often likely to metastasize to the internal organs and lymph nodes. 77 percent of all skin cancer-related deaths are due to melanoma, according to the American Academy of Dermatology. Being able to recognize this cancer when it is in its very early stages is crucial in surviving this skin cancer.
Metastasis
Every patient who has been treated for this cancer is at risk for it spreading. However, when the original tumor (primary melanoma) is less than one millimeter thick (considered thin), removing it surgically has a 95 percent cure rate, due to it being confined to the top skin layers and being unlikely to spread, according to the American Academy of Dermatology. However, it is important to keep in mind that five percent of thin melanomas are not completely cured when removed surgically, so it is important that patients go to all scheduled doctor’s appointments and regularly do their self-examinations of their skin, as well as their lymph nodes.
When it is suspected that this cancer has spread, diagnostic testing will be done to determine if it has spread, and to where it has spread. Once this cancer has spread to the lymph nodes located closest to the original tumor, there is a chance that it will spread to other organs and lymph nodes. Once this cancer has spread to other organs and lymph nodes, it is in stage IV, which always has a poor prognosis. Treatment including chemotherapy, radiation therapy, selective surgical excision and immunotherapy, is often given in stage IV, but they are not guaranteed to cure this cancer. Stage IV melanoma patients can survive, but the odds are not good in many cases.
So, how fast does melanoma spread? This is an unanswerable question. However, there are statistics available through the American Academy of Dermatology explaining the likelihood of melanoma spreading to other organs. These statistics are as follows:
- Other areas of skin and lymph nodes: 50 to 75 percent
- Liver: 54 to 77 percent
- Bone: 23 to 49 percent
- Heart: 40 to 45 percent
- Adrenal glands: 36 to 54 percent
- Thyroid: 25 to 39 percent
- Lungs and between the lungs: 70 to 87 percent
- Brain: 36 to 54 percent
- Gastrointestinal tract: 26 to 58 percent
- Pancreas: 38 to 53 percent
- Kidneys: 35 to 48 percent
What Affects How Fast Melanoma Spreads?
The type of melanoma makes a difference. When the cancer cells invade the deeper skin layers, known as invasive melanoma, it spreads faster, grows faster and is the most dangerous. Superficial melanomas and Lentigo maligna melanomas grow more slowly, are often easier to treat, and have a higher cure rate than invasive melanoma, when diagnosed in an early stage.
Certain genetic changes can affect how quickly this cancer spreads. Certain gene abnormalities encourage this cancer to invade surrounding tissue. People who have two copies of the cyclin variant were at an 80 percent higher risk of developing melanoma.
The composition of abnormal cells, or the grade of cancer, can result in melanoma spreading faster. When high grade cancer is present and very abnormal cells make up the tumor, this cancer most often spreads and grows very fast. Low grade cancer in which the tumor is made of cells that only slightly differ from normal cells, most often grow slowly, and in some cases, do not spread at all.
Resources
American Academy of Dermatology. (2010). Four Types of Melanoma. Retrieved on August 30, 2010 from the American Academy of Dermatology: https://www.skincarephysicians.com/skincancernet/four_types.html
University of Maryland Medical Center. (2009). Melanoma and Other Skin Cancers – Introduction. Retrieved on August 30, 2010 from the University of Maryland Medical Center: https://www.umm.edu/patiented/articles/what_melanoma_000032_1.htm
Image Credits
Melanoma: United States Federal Government - Wikimedia Commons Public Domain