Types of Melanoma: Listing the Four Types of Melanoma
What is Melanoma?
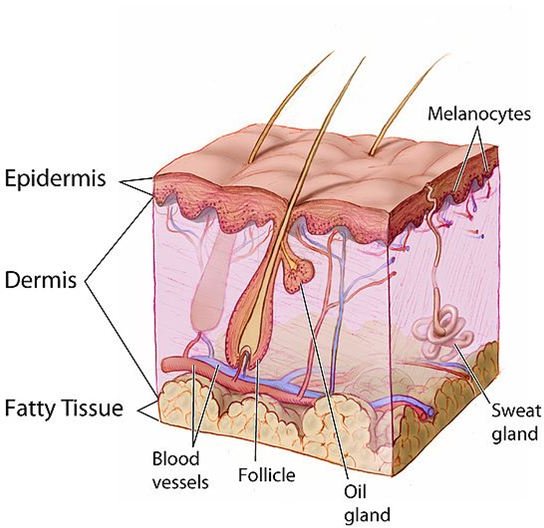
Melanoma is skin cancer. Skin, the largest organ of the body, has two layers: the dermis and epidermis. The dermis involves the inner layers of skin and house lymph and blood vessels, hair follicles and glands. The epidermis is made up of cells referred to as squamous cells. Basal cells are underneath the squamous cells. Melanocytes, the pigment cells, are found in the deepest part of the epidermis.
Melanoma begins in the cellular level and occurs when melanocytes become malignant. There are four types of melanoma: superficial spreading melanoma, acral lentiginous melanoma, nodular melanoma and lentigo maligna.
Superficina Spreading Melanoma
Superficial spreading melanoma (SSM) is responsible for 60 to 70% of all skin cancer cases. This is the most common form of melanoma seen in young people, and in young people usually appears after puberty. SSM is often seen as a slightly raised or flat, dark area on the skin with a blotched color appearance. The borders are erratic and can appear to have indentions. SSM is a cancer that spreads very slowly. Superficial spreading melanoma often appears on the chin in women, and on the back or front of legs in men. SSM also is seen on the soles of the feet.
SSM, initially, is a thin lesion that is on the epidermis. This stage can last for years. If not detected, the lesion begins to grow vertically, and into the dermis. When SSM reaches this stage, the prognosis grows worse. Once the cancer has reached the dermis, this is a dangerous condition as the cancer can begin to invade other tissues.
Acral Lentigous Melanoma
Acral lentigous melanoma (ALM) is a relatively common type of skin cancer in people with darker skin tones. This type of melanoma is often seen on the soles of the feet, nail beds, and palms of hands. It usually appears as a flat or raised, dark or multi colored lesion with erratic borders. When ALM is located on the big toe or thumb, it can present as a black line across the nail. It may invade the cuticle, causing it to be discolored.
ALM grows slowly and in a linear fashion. If not treated, it will slowly penetrate the skin’s dermis layers, and becomes a much more serious cancer to treat.
Nodular Melanoma
Nodular Melanoma (NM) accounts for 15 to 30% of the four types of melanomas. NM is often found on the head, neck and torso. It often appears as a raised dark bluish/black growth, however, in some cases the lesions are red or pink. The nodule is often round and small. This form of cancer in seen more often in men than in weomen.
Nodular melanoma grows quickly and has often invaded deeper layers of tissue upon diagnosis. It normally grows on the skin rather than from a mole or nevus. This form of melanoma is more common in middle aged people and those who have been known to have frequent sun exposure.
Lentigo Maligna Melanoma (LMM)
Lentigo maligna melanoma (LMM) is the rarest form of melanoma. It is more common in older people, and usually develops on the face. It appears as a dark or tan color, and is usually flat. LMM grows very slowly and does not grow down into deeper tissues as other melanomas tend to do.
Treatment of Melanoma
Treatment of melanoma can involve surgery, radiation, chemotherapy or drug treatment. The doctor is the one who will review your case, your cancer, the stage of cancer and determine the best treatment plan.
Your doctor should answer any questions you may have such as side effects, prognosis, and length of treatment.
As a patient, you can request more than one opinion on your melanoma and proceed with the doctor and treatment that you are most comfortable with.
Image Credits
Image Credit: Wikimedia Commons/Don Bliss