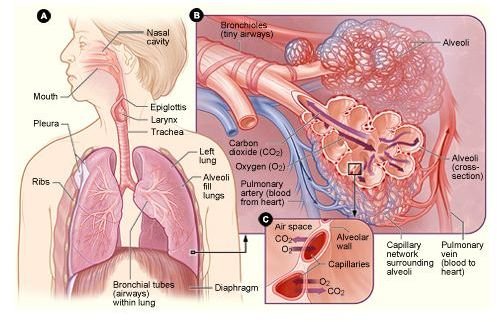
Non Small Cell Lung Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment.
According to the World Health Organization, cancer is the leading cause of death. Lung cancer alone is responsible for 1.3 million deaths worldwide. Tobacco use is the most important risk factor for different types of cancers. Long term exposure to tobacco smoke is the primary cause of lung cancer. There are two basic types of lung cancer: small cell lung carcinoma and non-small cell lung carcinoma. The later is the most prevalent type of lung cancer (aprox. 80%).
Causes
When a cell lose the ability to control its growth and cell division processes then a cancerous cell is born with he development of a tumor. The principal cause of many type of cancers is the exposure to carcinogens. Tobacco smoke has many chemicals (it has more than 60 known carcinogens: nitrosamine, benzopyrene, radon decay by products, etc) that may act as carcinogens. Genetic predisposition, exposure to asbestos, and pollution are also high risk factor for the development of many types of lung cancer including the non small cell lung cancer
Signs and Symptoms
The following represent signs and symptoms of this type of cancer (according to the National Institute of Cancer):
- A cough that doesn’t go away.
- Trouble breathing.
- Chest discomfort.
- Wheezing.
- Streaks of blood in sputum (mucus coughed up from the lungs).
- Hoarseness.
- Loss of appetite.
- Weight loss for no known reason.
- Feeling very tired.
Diagnosis Methods
A doctor may order a variety of blood or other tests to accurately diagnose the presence of non small cell lung cancer in a suspected patient. A chest X-ray and CT (computed tomography) scan are standards test to diagnose this type of cancer. Finally a biopsy may be order for further histological confirmation.
Available Treatment Options
Treatments for this type of disease include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy, depending on the overall evaluation of the patient. If the tumor is localized then surgery may be an option. If it has spread to the point where it cannot be managed surgically, then radiotherapy and chemotherapy may be performed.
Radiotherapy is the use of use of radiation to kill cancer cells. It is with a potent X-ray machine. Chemotherapy refers of the use of chemicals drugs kill the liver tumor cells or to prevent the growth of the tumor. According to Clegg et al ( 2002 ) paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine are all approved drugs for treatment of this cancer type.
References:
National Cancer Institute: https://www.cancer.gov/
World Health Organization: https://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs297/en/
National Institutes of Health: www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/.../007194.htm
Clegg et al (2002) . Clinical and cost effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine, and vinorelbine in non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review. (available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11809985)
Image credit:
NAtional Institutes of Health : https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/dci/images/lung_anatomy.jpg