Learn about Alcoholic Cardiomyopathy
Alcoholic Cardiomyopathy and its Causes
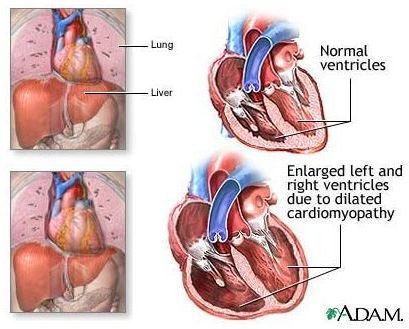
Alcoholic cardiomyopathy is a heart disorder resulting from excessive intake of alcohol over a long period. The disorder enables you to have a weakened heart owing to toxic effect of binge drinking and heavy alcohol use. If you are an alcoholic, your heart muscle might eventually weaken because the heart can neither pump enough blood effectively, nor keep electrical rhythm normally. The heart dilates and the heart muscle declines to work properly leading to heart failure and heart valve problems. Poor diet also exacerbates this condition. Click on image to enlarge.
Symptoms
Understanding the symptoms of cardiomyopathy is essential to allow you to recognize this condition. Signs and symptoms of this heart disorder include:
• Loss of appetite
• Breathing difficulty when lying flat
• Breathing difficulty in the middle of the night
• Weight gain
• Fatigue
• Cough with frothy pink material
• Swollen stomach, legs, feet, and ankles
• Abnormal sound during a heartbeat known as heart murmur
• Rapid and irregular pulse
• Weakness, faintness, and nausea after physical activity
• Decreased urine
• Sensation of urinating at night
Tests and Examinations
If you experience those symptoms, you can have one of these tests performed:
Chest X-ray
Chest x-ray or chest CT can enable you to know if your heart dilates by taking pictures of the appearance of blood vessels in your lungs and heart. It can also show fluid accumulation in the lungs and heart valves.
Echocardiography
Echocardiography or ECHO produces a moving picture of your heart by using sound waves. It features your heart’s shape and size to decide whether your heart performs well. This test includes a transesophageal echocardiogram, which features a picture of the back of your heart. Another one is a stress echocardiogram or stress echo to feature an indication of coronary artery disease.
Electrocardiogram
Electrocardiogram or EKG can demonstrate the stable or unstable electrical rhythm of your heartbeat in exquisite detail. This test also finds any damage of the heart and measures either the position or size of your heart chambers.
Stress Tests
Stress tests include echocardiography, positron emission tomography (PET), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and nuclear heart scanning. You must take some workouts to make your heart beat fast during stress tests because they can evidently analyze heart problems while your heart is palpitating.
Medical Procedures
It is essential to have one or more diagnostic procedures to corroborate a diagnosis including:
Cardiac catheterization
Your physician injects local anesthetics to numb the area and inserts an intravenous (IV) line into a blood vessel in your arm, neck, or groin. A catheter, which is a long and flexible tube, is inserted through the IV and into your blood vessel. He or she then threads the catheter into your heart with the help of x-ray machine. The physician then acquires blood samples from the heart, analyzing the coronary arteries with fluoroscopy (an x-ray technique). This technique enables your physician to perform a myocardial biopsy on the heart muscle.
Myocardial biopsy
During cardiac catheterization, the physician removes small pieces of tissue from the heart muscle by using a special device with jaws on the tip. Then, a microscope can help determine if there are cellular changes in the heart.
Coronary angiography
This procedure is performed with cardiac catheterization by injecting a special dye into your coronary arteries. The dye is so visible on an x-ray that your physician can scrutinize blood flow through your heart. Alternatively, the physician can inject the dye into heart chambers to examine if your heart pumps blood properly.
Treatments
Your physician might recommend some treatments including:
• Lifestyle changes by avoiding excessive alcohol intake and exercise regularly
• Medicines such as beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, and diuretics
• Surgical procedure such as heart transplant
• Non-surgical procedure known as alcohol septal ablation
References
The National Health Lung and Blood Institute: What is Cardiomyopathy? - https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/dci/Diseases/cm/cm_types.html
Floridahealthfinder.gov: Alcoholic Cardiomyopathy - https://www.floridahealthfinder.gov/health-encyclopedia/Health%20Illustrated%20Encyclopedia/1/000174.shtml
eMedicine.medscape.com: Treatment and Medication - https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/152379-treatment
University of Colorado Hospital: Cardiomyopathy - https://www.uch.edu/conditions/heart-circulation-conditions/cardiomyopathy/patient-education/index.aspx
Photo Credit
Image courtesy of the National Library of Medicine.
Disclaimer
Please read this disclaimer regarding the information contained within this article.