What Are Hives? An Overview of This Allergic Skin Disorder
Overview
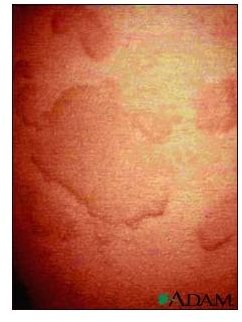
Your body releases a protein called histamine and some other chemicals into the bloodstream once you have an allergic reaction to a substance. At this time your body discharges histamine and your tiny blood vessels (capillaries) leak fluid. It builds up in the skin, leading to itchy, red, swollen welts on the skin surface, which are the common conditions of hives. Click on image to enlarge.
They vary in sizes and shapes, ranging from a coin to a plate. Women are more susceptible to suffer from hives than men. This skin rash is prone to move around and get bigger swiftly, vanishing in a specific place and coming back in other areas of the body, including your face, ears, lips, tongue, and throat. Please avoid scratching because it will only spread the inflammation.
There are two types of urticaria: acute urticaria and chronic urticaria. The acute commonly lasts less than six weeks, while the chronic one usually proceeds more than six to eight weeks.
Some substances can result in hives such as medications (usually antibiotics and aspirin), insect bites, animal dander (cats), milk, eggs, nuts, fish, and shellfish.
A condition that accompanies hives at times is angioedema, which is deep swelling occurring beneath the skin instead of on the surface. Your eyes, lips, hands or feet are swollen when you have angioedema.
Symptoms
In addition to being swollen, red and itchy, urticaria might commonly become visible in the morning, go away around lunchtime, and reappear for the rest of the day. You may find this skin rash irritating. It is recommended you take a picture once you have this rash to present to your health-care provider because this can come and go rapidly. He or she might analyze you based on your symptom history even though you provide no proof.
Treatment
Acute urticaria requires no treatment. But if the symptoms are severe, there are several helpful medications to cope with them such as:
Antihistamines
Antihistamines, as the name suggests, can obstruct the amount and effects of histamines, helping relieve the itching and rash. Beware of these medications when you would like to drive a car as they can possibly cause sleepiness. However, if you have sleeping problem related to itchiness, you can take advantage of antihistamines.
It is not recommended that pregnant women take these medications. Sometimes, health-care providers may suggest a kind of antihistamines known as chlorphenamine, which is believed not to affect the unborn baby.
Corticosteroids
High-dose corticosteroids taken orally can restrain the immune system leading to ease the symptoms of itchiness. Keep in mind you do not take these medications for longer than 5 days because the increasing risks of infection may occur. Consult your health-care provider for more info.
If you suffer from chronic urticaria you need to have the following treatments:
Antihistamines and Corticosteroids
As abovementioned, those are effective to help alleviate the symptoms.
Diet
In this treatment you need to avoid foods that activate histamine such as tomatoes, fish, spinach, chocolate, yogurt and strawberries.
Menthol and Camphor Cream
They are good treatments to reduce itchiness, although they are sometimes less effective than other medications. Menthol and camphor can help numb nerve endings.
Avoid Stress and Alcohol
It’s recommended to keep away from stress and alcohol if you have hives, as they can exacerbate your symptoms.
References
Medicalnewstoday.com: What Are Hives? What Is Urticaria? What Causes Hives?
Medicinenet.com: Hives (Urticaria & Angioedema)
The University of Maryland Medical Center: Hives (Overview)
Photo Credit
Image courtesy of the National Library of Medicine