How Do Ovulation Tests Work?
What is Ovulation Testing?
Before you can understand the answer to the question, “How do ovulation tests work?” you must first understand what one of these tests does. Ovulation testing is the process by which a device helps a woman determine her time of ovulation each month. This designed to assist the woman in finding the most likely time in which she is fertile. Due to the fact that many females have difficulties getting pregnant, an ovulation test will give them a better idea of when to perform intercourse or attempt a controlled fertilization.
Over the course of a standard menstrual cycle, a woman has the tendency to ovulate around day 14, halfway through the process. However, this can be greatly impacted if a woman has irregular cycles or is subject to other factors such as high stress situations. This makes ovulation take place anywhere up to a week before or after it normally should. Researchers have also found that ovulation is directly associated with the length of the menstrual cycle. For example, a woman with a longer cycle are more likely to ovulate later on while women with shorter cycles will drop eggs earlier.
The Process of Identifying Fertilization
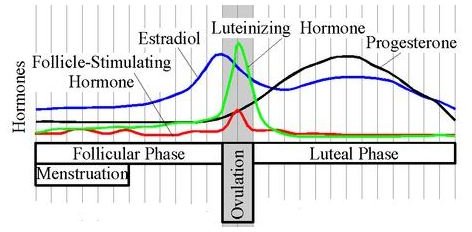
When a woman’s body is operating according to normal parameters, ovulation is properly controlled by follicle stimulating hormones (FSH). FSH promotes the growth of an ovum on a follicle in the ovaries. In the most basic sense, her body will produce luteinizing hormone (LH) that signals the separation of the egg from the follicle. The fallopian tube uses cilia to brush the ovaries, helping the egg to become disengaged. At this point, the woman is ready for fertilization.
While the LH is produced throughout the menstrual cycle, it increases significantly during ovulation. Since this surge in hormones is so brief, a woman needs to ensure that the test is conducted at the right time of the month and at the right moment of the day. The majority of LH is produced after a woman wakes up, so testing in the morning is not as efficient as is the afternoon. An ovulation test kit is exposed to urine from the woman. The test itself holds anti-LH antibodies, used to sense the presence of the hormone.
Following identification by the LH tester, a woman has roughly 36 hours to successfully become fertilized. However, this period can be even shorter since many eggs only have about a 24 hour life span. If the egg has already dropped at the time of testing, a woman may only have a brief chance to become pregnant.
Ovulation Test Formats
There are two different format of tests designed to identify ovulation. One is simply a test strip that is placed inside a vial of urine. The other is held midstream similar to a pregnancy test. Both are considered reliable predictors of ovulation. Usually, the time frame for a successful test is merely five minutes or so. Two lines of color bands are used on the test. One is a control line, which informs the woman the test is working. The other is designed to identify if ovulation is occurring. If both lines appear, then the woman is in ovulation, if only one appears, she is not.
Planning for a pregnancy can be a challenge in many ways, some more complex and life-changing than simply the process of actually getting pregnant. In order to make this process more efficient, its important to take note you understand the answer to the question “How do ovulation tests work?”
References
“How Ovulation Testing Kits Work” Ovulation Calculator: https://www.ovulation-calculator.com/ovulation-tests/ovulation-tests.htm
“How Ovulation Tests Work” Baby Hopes: https://www.babyhopes.com/articles/ovulation-test-work.html
Image Source
Menstrual Cycel. (Supplied by Ekem at Wikimedia Commons; Creative Commons 2.0; https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/1/16/Estradiol.Cycle.JPG)