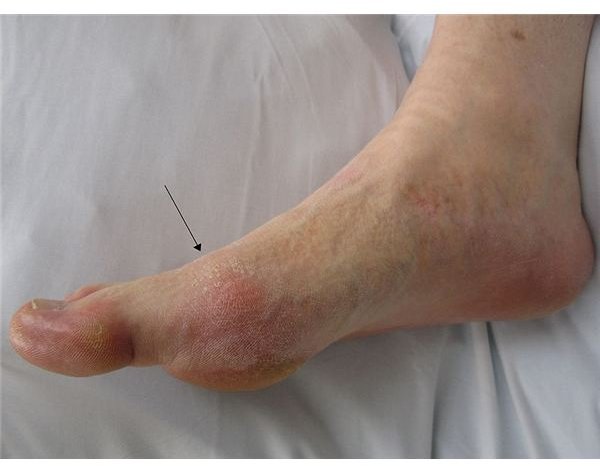
How Does Colchicine Gout Treatment Works?
Overview
Colchicine, a medication prescribed for gout treatment, comes from dried seeds of the meadow saffron plant. Aside from gout, it is also used in the treatment of patients with familial Mediterranean Fever. It is in .5 mg and .6 mg tablet forms and should be taken orally. This drug, considered as an anti-gout agent, is usually not prescribed to relieve pain.
Colchicine gout treatment works by stopping the entry of inflammatory cells into the affected joint area, thus reducing inflammation and pain. It is prescribed for acute attacks of gout, and is usually taken as soon as the first signs of joint pains occur to prevent further discomfort. It may also be used in between gout attacks as a preventive measure.
While colchicine may not frequently work for every person with gout attacks, it carries a respectable 75% gout pain reduction at least 12 hours after taking of the medication. Inflammation of the gout usually subsides a day or two after taking the said medication. If no relief is experienced after a few days treatment, it is important that patients should let their physician know about this for further evaluation or dosage modification.
Who Should Not Take It
People who have certain diseases such as liver, kidney and bone marrow ailments are advised never to take this medication. It is also not recommended as a medicine for other types of pain. Elderly patients as well as patients having low count of white blood cells are also not prescribed with this medication. This medication is also contraindicated in pregnant women and breastfeeding mothers.
Side Effects
The possible side effects of colchicine for gout pain include vomiting, abdominal cramps, diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. Diarrhea is the most recurring side effect seen in people who have taken colchicine. When this occurs, patients should inform their specialist immediately. The use of other drugs can also heighten the risks of side effects of colchicine. Likewise, it is not recommended for patients to eat grapefruit if they are taking this drug. Colchicine gout treatment among pregnant women is only recommended if the benefits of the medication outweigh the possible risks of using it.
More serious side-effects include depression of the bone marrow, with some patients showing low platelet counts, low white blood cell counts and aplastic anemia during long term use. Hair loss, nerve pains and muscle pains may also manifest. Some men may experience azoospermia, or absence of sperm, which is often reversible once he is off the medication.
Overdosage
Overdosage can sometimes happen. This is why patients should strictly follow their doctors prescription on how to take colchicine. Symptoms of overdosage include easy bruising, infections, paleness, vomiting, nausea, diarrhea, and slow heartbeat. Patients should be brought to emergency care if these are observed.
References
RxList: Colchicine
MedicineNet.com: Medications and Drugs
MedlinePlus: Colchicine
Image Credit / Wikimedia Commons / Jmh649