Common Oral Cancer Symptoms
Oral cancer is the cancer that occurs on the lips, inside the mouth, on the back of the throat, the tonsils or salivary glands. It mostly strikes people over 40, with two men affected with this disease for every women affected. Those who smoke, consume alcohol, or chew tobacco are most susceptible to this cancer. The other major risk factors include exposure to sun, sexual transmission of the human papilloma virus, and history of other cancers.
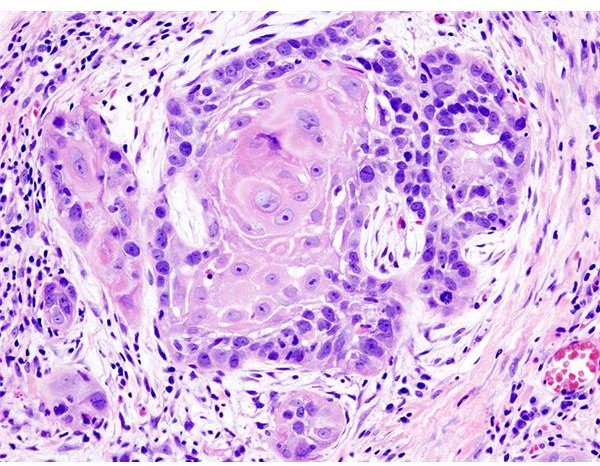
Most oral cancers begin in the flat squamous cells that cover the surfaces of the mouth, tongue, and lips, and spreads through the lymphatic system.
Image Credit: Wikimedia Commons
Patches
The most common of oral cancer symptoms is white, red, or a mixture of white and red patches on the mouth or lips.
Erythroplakia or red patches, and Erythroleukoplakia or a mixture of red and white patches are the most dangerous. Most of such patches turn malignant or progressively worse. Leukoplakia or white patches occur more frequently than red or mixed patches, but the chances of them turning malignant is comparatively less. White patches usually remain harmless, though some of them do turn malignant.
Apart from patches, a sore or blister on the lip or in mouth that bleeds and does not heal could also be a sign of oral cancer.
Other Symptoms
At times, oral cancer come with any of the following symptoms. Apart from patches, the common signs and symptoms of oral cancer include:
- Frequent bleeding in the mouth for no apparent reason
- Teeth becoming loose
- Swelling of the jaws, causing difficulty in wearing dentures
- Unexplained pain in the mouth, especially when swallowing, speaking, or chewing
- Lump or wart like mass inside the mouth or neck, felt with the tongue, or a feeling that something is caught in the throat with no known cause
- Hoarseness which lasts for a long time, or change in voice
- Numbness or loss of feeling in the oral and facial region
- Unilateral and persistent ear aches
Dangers
The symptoms of oral cancer are not exclusive to the diseases, and very often the early signs of oral cancer is mistaken for some other common infection . The white and red patches are often mistaken as canker sores, and the sores, bleeding and the like could all be the result on a simple bite rather than dangerous tissue change. This raises the danger of the oral cancer remaining undetected in the early stages.
The way to confirm whether the signs indicate oral cancer is to visit a doctor or a dentist, especially when the symptoms persist for more than 14 days. The medical practitioner makes a careful examination of the mouth, throat, cheeks, and lips, and undertakes biopsy to check for cancer.
Oral cancer can become fatal if not detected in its early stages. The disease has a five-year survival rate of about 50 percent.
Disclaimer
This article does not constitute medical advice and is not intended to treat or diagnose. Please consult a medical practitioner to check for signs and symptoms of oral cancer.
Reference
- Medicinenet.com. Oral Cancer. https://www.medicinenet.com/oral_cancer/page4.htm
- Oral Cancer Foundation. Oral Cancer Facts. https://www.oralcancerfoundation.org/facts/index.htm
- National Cancer Society. What You Need to Know About Oral Cancer. https://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/wyntk/oral/page5